
The padel serve is a mandatory underhand stroke that must be struck at or below waist height after a single bounce behind the service line to initiate every point. Many players struggle with unforced errors or illegal motions that immediately put them on the defensive. This lack of precision allows opponents to control the net early, turning what should be a neutral start into a lost game. By mastering the specific padel serve rules, you can transform your service game into a tactical weapon.
What Are the Official Padel Serve Rules for Legal Play?

Official padel serve rules mandate that the server must keep both feet behind the service line and hit the ball underhand into the diagonal service box. This foundational requirement ensures the game remains focused on rallies rather than overwhelming service power. Failing to adhere to these boundaries results in a fault, giving the receiver an unearned advantage.
Where Should the Server Stand?
The server must stand behind the service line, between the center line and the side wall. Both feet must remain in this zone until the ball is struck to avoid a technical foot fault.
What Is the Correct Hitting Height?
The ball must be hit at or below the waist level, which is generally considered the height of the player’s belly button. If you crouch during the motion, the legal hitting point also lowers accordingly.
- Both feet must be behind the service line.
- The ball must bounce once before contact.
- The racket must make contact below the waist.
- The serve must cross the net into the diagonal box.
But that is not all.
The ball may hit the opponent’s side wall after the bounce, but it cannot touch the wire mesh fence. Understanding these nuances is critical for competitive play.
Key Takeaway: Strict adherence to positioning and height regulations is the first step toward a legal and effective service game.
| Requirement | Rule Detail | Penalty |
|---|---|---|
| Feet Position | Both behind service line | Foot Fault |
| Contact Height | Below the waist/belly button | Technical Fault |
| Landing Zone | Diagonal service box | Service Fault |
Maintaining legal mechanics prevents the loss of points before the rally even begins.
How Do You Master the Basics of the Padel Serve?

Mastering the basics requires a consistent “drop and hit” motion that emphasizes accuracy over pure velocity. According to the padel serve rules, you have two chances to get the ball into play, making a reliable second serve essential. Beginners should focus on a smooth follow-through to ensure the ball clears the net comfortably every time.
How Do You Perform a Perfect Ball Drop?
Hold the ball at waist height and let it fall naturally without throwing it upward or slamming it down. This ensures a consistent bounce height, allowing your racket to meet the ball at the ideal strike zone.
What Is the Best Follow-Through Motion?
Your racket should continue its path toward the target box even after contact is made. This momentum not only improves accuracy but also prepares you to move forward toward the net immediately.
- Keep your eyes on the ball through contact.
- Transfer weight from the back foot to the front foot.
- Maintain a relaxed grip for better control.
Here is why this matters:
A repeatable motion reduces the mental pressure during tight games. If your basics are solid, your first serve becomes a tool for aggression rather than a source of anxiety.
Key Takeaway: A controlled ball drop combined with a natural weight transfer creates the foundation for service consistency.
| Phase | Technical Focus | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| The Drop | Gravity-fed release | Consistent strike height |
| The Strike | Clean underhand contact | Legal ball trajectory |
| The Finish | Forward momentum | Faster transition to net |
Consistent basics allow you to focus on strategy rather than just keeping the ball in play.
Why Is Placement More Important Than Power?
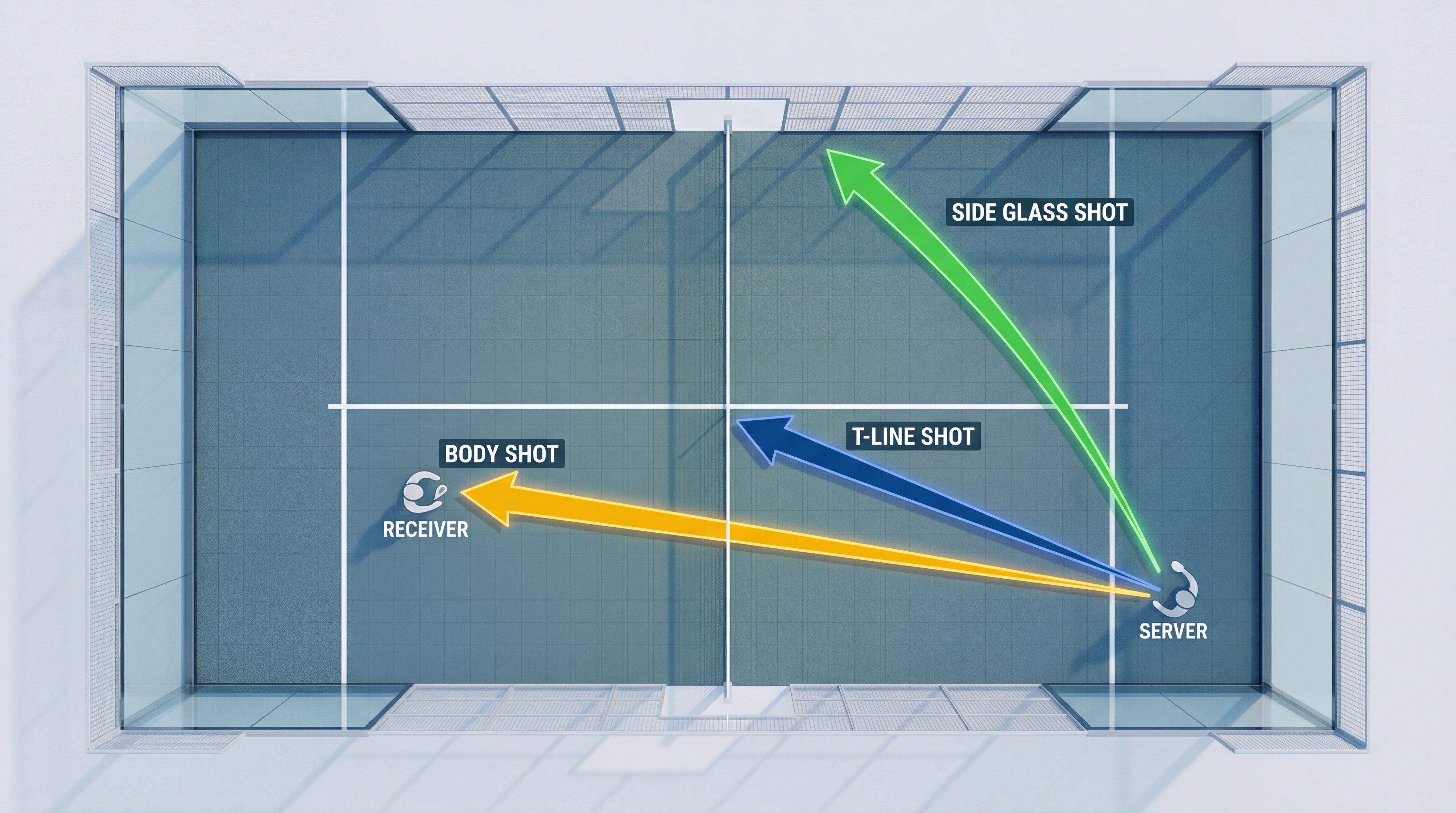
Strategic placement is the primary method used to disrupt a receiver’s rhythm while following the padel serve rules. Because the court is enclosed, a well-placed ball that hits the glass at a difficult angle is far harder to return than a fast ball hit directly at the opponent. You should aim for targets that force the receiver into uncomfortable movements.
Why Target the Side Glass?
Hitting the side glass creates an unpredictable bounce that forces the receiver to move laterally and react quickly. When the ball “dies” off the glass, the opponent is often forced to produce a weak, defensive lob.
How Does the T-Line Serve Work?
Serving close to the center “T” limits the angles available to the receiver for their return. It keeps the ball away from the glass but forces the opponent to stay honest and not lean too far toward the side wall.
- Aim for the corners near the glass.
- Target the opponent’s body to jam their swing.
- Use the “T” to vary your angles.
But wait, there’s more.
Mixing your targets keeps the opposition guessing and prevents them from camping in one spot. A predictable server is an easy target for aggressive returns.
Key Takeaway: Utilizing the glass and the T-line as targets is more effective for winning points than hitting the ball hard.
| Target Zone | Strategic Goal | Difficulty for Receiver |
|---|---|---|
| Side Glass | Unpredictable bounce | High |
| Center T-Line | Narrow return angles | Medium |
| Body Shot | Jamming the swing | High |
Placement forces the opponent to play your game, giving you control over the transition to the net.
How Can You Vary Speed and Spin for Better Results?

Varying your speed and spin is a legal way to exploit the padel serve rules and keep your opponents off-balance. By applying slice (backspin), you can make the ball stay lower after the bounce, making it nearly impossible for the receiver to hit an aggressive return. Flat serves, while faster, should be used as a surprise element to catch the opponent off-guard.
How Do You Add Slice to Your Serve?
Brush the back and bottom of the ball with an open racket face during contact. This creates backspin, causing the ball to “slide” on the turf and stay low after hitting the glass.
When Should You Use a Flat Serve?
Use a flat, faster serve when you notice the receiver is standing too far back or anticipating a slow slice. The lack of spin allows the ball to travel faster, forcing a hurried reaction from the opponent.
- Slice keeps the ball low.
- Side-spin makes the ball kick laterally.
- Flat serves increase raw velocity.
But that is not all.
Mastering spin allows you to control how the ball interacts with the environment. A ball with heavy side-spin can jump unexpectedly off the back glass, leading to an immediate ace or a forced error.
Key Takeaway: Alternating between heavy slice and flat serves prevents the receiver from timing your delivery effectively.
| Spin Type | Ball Behavior | Strategic Use |
|---|---|---|
| Backspin (Slice) | Stays low and skids | Standard tactical serve |
| Side-spin | Curves and kicks laterally | Disruptive variation |
| Flat | Fast and direct | Surprise change-up |
Variation in pace and rotation is the hallmark of an advanced server who understands the mechanics of the game.
How Do You Build a Consistent Pre-Serve Routine?

Building a pre-serve routine is essential for maintaining focus and ensuring your mechanics stay within the padel serve rules. A ritual serves as a mental reset, helping you to execute the same motion whether you are winning or losing. Consistency in your setup leads directly to consistency in your delivery.
What Should a Routine Include?
A good routine often includes bouncing the ball a set number of times and checking your opponent’s positioning. These few seconds allow you to visualize your target and commit to a specific type of serve.
How Does Breathing Help Your Serve?
Taking a deep, controlled breath before starting your motion lowers your heart rate and stabilizes your hands. This prevents the “rushed” feeling that often leads to double faults or technical infractions.
- Bounce the ball 2-3 times.
- Check the receiver’s location.
- Take one deep breath.
- Visualize the landing spot.
Here is the deal:
Players who rush their serve are far more likely to commit foot faults. A routine forces you to slow down and verify that your feet are legally placed behind the line.
Key Takeaway: A structured ritual settles nerves and ensures that every serve is executed with tactical intent.
| Routine Step | Purpose | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Ball Bouncing | Rhythmic focus | Mental grounding |
| Visual Check | Tactical assessment | Better target selection |
| Deep Breath | Physical relaxation | Smoother stroke |
Consistency is the result of repetition; a routine makes that repetition automatic.
What Is the Role of Mental Preparation in Serving?

Mental preparation allows you to execute the padel serve rules under extreme pressure, such as during break points or tie-breakers. Since the server has total control over the start of the point, the psychological burden is often higher than during the rally. You must learn to focus on the process of serving rather than the potential outcome of the point.
How Do You Handle Second Serve Pressure?
Treat the second serve with the same confidence as the first by picking a safe, high-percentage target like the center of the box. Avoiding the “fear of missing” is key to preventing the double faults that lose matches.
Can Visualization Improve Accuracy?
Mentally rehearsing the flight of the ball and its bounce off the glass before you swing significantly increases your success rate. Visualization bridges the gap between your physical skills and your tactical goals.
- Focus on the “drop and hit” rhythm.
- Ignore the crowd or the score.
- Trust your practiced mechanics.
But that is not all.
Positive self-talk can prevent the frustration that follows a first-serve fault. Remind yourself that you have already practiced this motion thousands of times.
Key Takeaway: Developing a strong mental game ensures that your physical skills don’t crumble when the score is close.
| Mental Tool | Application | Objective |
|---|---|---|
| Visualization | Pre-hit imagery | Increased accuracy |
| Process Focus | During the motion | Reduced anxiety |
| Self-Talk | Between serves | Emotional reset |
A calm mind is your best asset when standing at the service line.
Which Practice Drills Improve Serve Accuracy?

Practice drills are the only way to internalize the padel serve rules so they become second nature during a match. You should dedicate time to hitting targets in the corners and practicing your transition to the net. Without deliberate practice, your serve will remain a liability rather than a strength.
What Is the Corner Target Drill?
Place cones or extra balls in the corners of the service box near the glass and attempt to hit them ten times in a row. This builds the precision needed to force difficult returns from your opponents.
How Does the Net-Rush Drill Work?
Practice serving and immediately sprinting to the net to hit a volley. This drill ensures that your service motion and your movement are integrated into one fluid sequence.
- Target practice for the glass corners.
- Second-serve reliability drills.
- Transition speed practice.
But wait, there’s more.
Recording your serve on video can help you identify if you are accidentally hitting the ball above your waist. Self-correction is much easier when you can actually see your technical errors.
Key Takeaway: Targeted drills turn a basic serve into a professional-level tactical delivery.
| Drill | Focus | Success Metric |
|---|---|---|
| Target Cones | Precision placement | 8/10 hits on target |
| Net Sprint | Transition speed | Reaching the volley line |
| Safety Drills | 2nd serve consistency | Zero double faults |
Deliberate practice ensures you can execute any serve under any condition.
Does Your Equipment Choice Impact Serve Compliance?

The right equipment makes it easier to stay within the padel serve rules while maximizing the effectiveness of your shots. A racket with a textured surface allows for better spin generation, while proper shoes provide the stability needed to avoid foot faults. Your gear should support your technical needs rather than hinder them.
Why Does Racket Surface Matter?
Rackets with a rough or sandy finish grip the ball better, making it easier to apply the slice required for a low-bouncing serve. A smooth racket may cause the ball to slip, resulting in a flatter, less effective delivery.
How Do Shoes Affect Your Serve?
Shoes with a herringbone sole pattern offer the best grip on the sand-filled turf used in most courts. This stability is crucial for maintaining a legal foot position and preventing accidental slides over the service line.
- Textured rackets for better spin.
- Balanced weight for control.
- Grip-focused shoes for stability.
Here is why this matters:
If you are constantly slipping, your contact point will be inconsistent. Proper footwear ensures that your base is solid, allowing for a legal and powerful delivery every time.
Key Takeaway: High-quality gear provides the physical foundation necessary for technical excellence and rule compliance.
| Equipment | Feature to Look For | Impact on Serve |
|---|---|---|
| Racket | Rough/Textured surface | Increased spin control |
| Shoes | Herringbone grip | Prevents foot faults |
| Balls | Proper pressure | Consistent bounce height |
Investing in the right tools allows your technique to shine without being held back by your gear.
How Does Court Construction Affect Your Strategy?

Understanding court construction is vital for applying padel serve rules to your tactical advantage. The way a ball bounces off different glass types or turf densities can change how you should approach your service game. You must adapt your targeting based on the specific physical properties of the court you are playing on.
How Do Glass Walls Vary?
Some glass walls are more “reactive” than others, meaning the ball will bounce further out or die more quickly. Testing the glass during your warm-up allows you to adjust your aim for the most difficult rebounds.
What Role Does the Turf Play?
Newer turf with more sand usually leads to a slower, lower bounce, which favors a heavily sliced serve. On faster, worn-down turf, a flat serve can be much more effective due to the increased ball speed.
- Test the glass rebound during warm-up.
- Observe sand density on the turf.
- Check net tension for “let” consistency.
But that is not all.
The lighting on the court can also affect how the receiver sees the ball. Serving from a shaded area into a bright spot can hide the rotation of the ball, making your spin even more effective.
Key Takeaway: Adapting your service style to the court’s physical conditions is a hallmark of an experienced player.
| Court Element | Strategic Adjustment | Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Glass Rebound | Adjust aim height | Maximum unpredictability |
| Turf Speed | Vary slice intensity | Keep the ball low |
| Ambient Light | Use shadows/angles | Disguise the ball’s spin |
The court is not just a surface; it is a tool you can use to enhance your serve’s effectiveness.
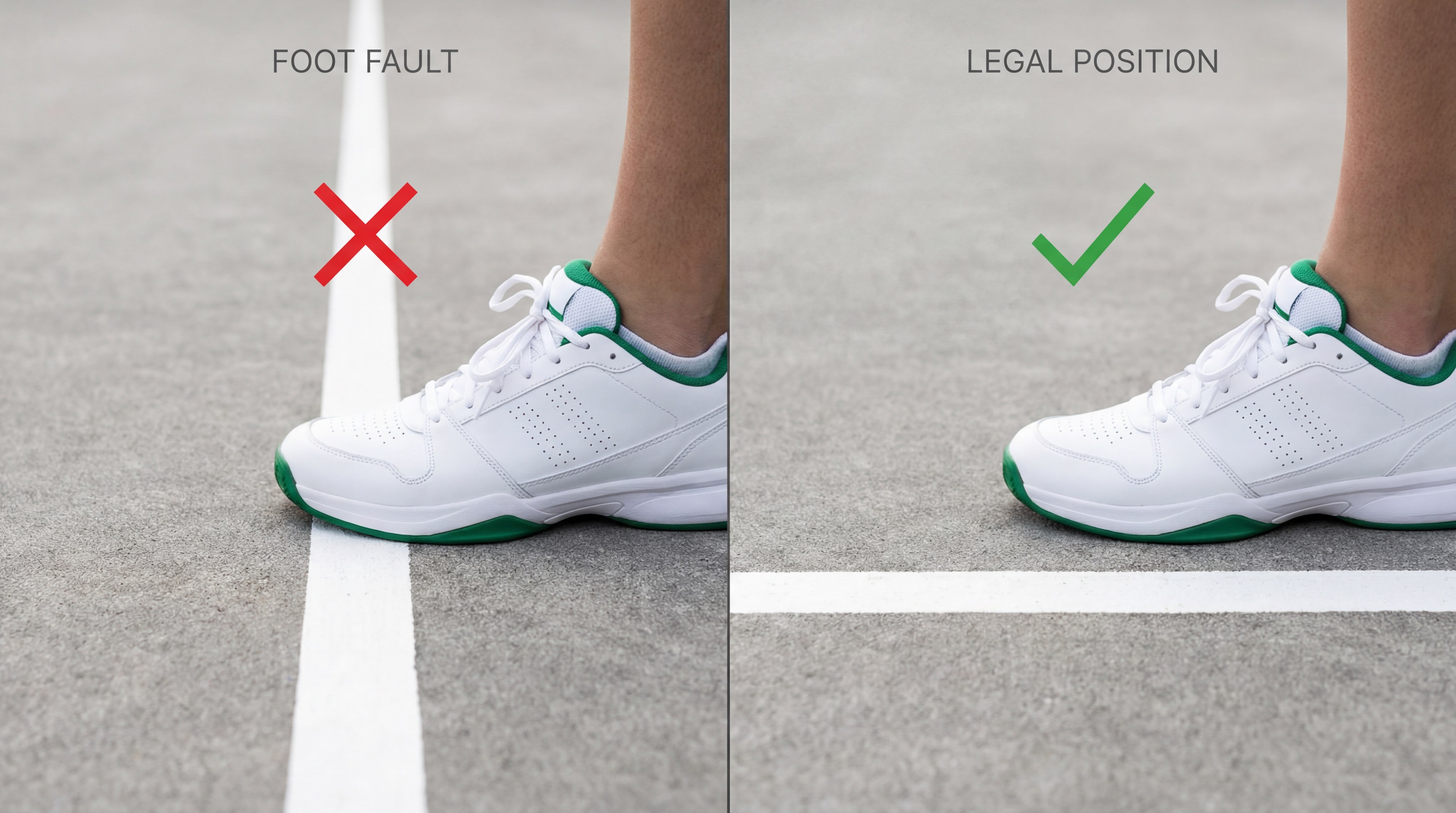
What Are the Most Common Serve Faults to Avoid?

Avoiding common faults is the most basic requirement of the padel serve rules, yet even experienced players occasionally make simple errors. Most faults are the result of losing focus or rushing the motion during high-pressure points. By identifying these common pitfalls, you can ensure that you never give away free points.
What Is a Technical Foot Fault?
A foot fault occurs when any part of your foot touches the service line or enters the court before you hit the ball. This is often caused by an over-eager attempt to rush to the net.
How Do High-Bounce Faults Happen?
If you drop the ball from too high or throw it downward, the bounce might exceed your waist level at the point of contact. This is an immediate technical fault that can be easily avoided with a gentle, gravity-fed drop.
- Stepping on the line (Foot Fault).
- Hitting above the waist.
- Ball hitting the mesh after the bounce.
- Serving into the wrong box.
But wait, there’s more.
A “let” is not a fault; it simply means you replay the serve. However, if the ball hits the net and then lands outside the service box, it is a fault. Knowing the difference prevents unnecessary confusion during a match.
Key Takeaway: Technical discipline and awareness of the rules prevent the unforced errors that decide close games.
| Common Fault | Typical Cause | How to Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Foot Fault | Rushing the net rush | Step back from the line |
| High Ball | Improper drop height | Release ball from waist level |
| Mesh Hit | Aiming too wide | Adjust aim toward the T-line |
Eliminating these errors allows you to maintain a high service hold percentage and keep the pressure on your opponents.
Mastering the serve is about balancing the strict requirements of the official rules with the creative possibilities of spin and placement. By treating every serve as a tactical opportunity rather than a mere formality, you can dictate the pace of every game. For more professional insights on equipment and training, contact us today to elevate your performance on the court.
FAQ
Can I serve the ball directly into the wire mesh?
No, the ball must bounce in the service box and can only hit the glass walls. Hitting the mesh after the bounce is an immediate fault.
What happens if the ball hits the net during a serve?
If the ball hits the net and lands in the correct service box, it is a “let” and the serve is replayed. If it lands outside, it is a fault.
Is it legal to serve with two hands?
While rare, the rules do not explicitly forbid a two-handed underhand serve, provided the contact point remains below the waist.
How many serves do I get in Padel?
Just like tennis, you get a first and a second serve. If you miss both, you lose the point.
Can I jump while serving?
No, the rules state that at least one foot must remain in contact with the ground at the moment of the strike to ensure a controlled underhand motion.